The ability for employees to work remotely from any location is a common feature of digital transformation programs, but different organisations have had varying levels of maturity. In 2020 COVID-19 has changed everything, dramatically increasing the proportion of employees working remotely, predominantly from home.
With the scaling-up of remote working, there has been a corresponding need to scale-up the measures that ensure remote working is carried out safely and securely. Maintaining digital workplace security has been extra important, as criminals seek to take advantage of the situation and target scams at people working from home.
With the profound changes of 2020, many organisations are now addressing the question of how to maintain security when employees work remotely. We see the need to rethink cybersecurity strategies for remote working as one of the top digital transformation trends for 2021. Organisations need to not only consider tools, policies and measures, but also how they can educate employees on being safe and secure when working remotely. In this article, we look at the issues around ensuring security when working remotely, as well as the steps that organisations need to take.
What are the security issues with remote working?
When the workforce is working remotely at scale, it presents new challenges to cybersecurity, IT and digital workplace teams with an increased risk of data breaches, malware incidents, phishing scams and even coordinated attacks.
Greater use of personal computers and devices
One reason for the elevated risk is the increased use of personal and unauthorised devices that may not have the same protection as corporate-issued hardware and may be used for both work and non-work purposes. For example, a personal laptop being used for work may have a virus on it or malware that puts sensitive data at risk. A personal laptop may also be used by other family members, including children, who may be less aware of security issues; the same may be the case for corporate-owned laptops. Other aspects of working from home such as Wi-Fi set-up can also be an area of risk.
Greater number of inexperienced users working remotely
Another issue is the greater number of people who are working from home, including less experienced users. For cybercriminals, more remote working simply means more opportunities – for example, during 2020 there has been a huge growth in Coronavirus-related phishing scams. For some, working remotely at home can also result in a different mindset where employees are less stringent in following corporate procedures like cybersecurity measures.
More shadow IT
Another key issue is an increased use of shadow IT for work purposes. With more people working remotely, more will work using applications that have not been authorised or reviewed by IT teams from a security perspective. Limiting the use of shadow IT among employees was already difficult, and even harder with a remote workforce.
Blurring of the sides of the firewall
A decade ago, it was easier for IT functions to pursue policies that focused on the idea of ‘perimeter security’, with a network firmly behind a firewall which can be easily protected. The concept has already been put under strain by the widespread use of cloud solutions and shadow IT, blurring the line between what is behind the firewall and what is not; remote working amplifies this even further.
Speed of roll-out of remote working
COVID-19 came about suddenly, meaning IT teams had to work at speed to roll out the necessary infrastructure and software to get everyone working remotely quickly. The pressure of the rapid rollout to maintain business continuity might have meant corners may have been cut, including the omission of potential robust cybersecurity measures.
Five tips to maintain security for remote working
Most IT functions will have dealt with some of the core actions around facilitating safer remote working in the past few months, for example extending VPN access and ensuring the necessary infrastructure and identity management set-up is in place. However, more actions may be required. Here are five tips to make sure you are sufficiently protected.
1. Review cybersecurity policies
With the new proportion of employees working from home, it is important for IT functions to review cybersecurity policies, taking into account any remote working security risks. Even if this is being done retrospectively, it is good practice to regularly assess any policies relating to IT security, as threats and working practices can change rapidly.
2. Review the security and settings of each of your applications
The suitability of commonly used applications should also be considered in light of any changes in cybersecurity policies, after which it should be assessed whether action needs to be taken, such as changing global settings to enforce multi-factor authentication, restrict access for certain roles, devices or networks with Conditional Access, or managing permissions and access to apps and information. You may also need to issue specific advice for users on risks associated with a particular application; it is often the detail that can have a significant impact on security issues with working remotely.
3. Use monitoring and detection systems where necessary
You may need to introduce some kind of additional monitoring and detection software to spot potential security threats. Any kind of monitoring which involves identifying the actions of individuals needs to navigate GDPR challenges and protect the data privacy of staff; it also needs to be explained carefully to employees to ensure there are no misunderstandings.
4. Create a cybersecurity awareness program for everyone working from home
Most cybersecurity issues are caused by employees, commonly originating from using unsupported software or ignoring advice from IT. It is also easy to fall for phishing scams which can be extremely sophisticated. Arguably, the single most important thing organisations can do to prevent such slip ups is to drive awareness of cybersecurity issues for everyone working remotely. This can be done through training, communications, phishing email drills, cybersecurity champions and more – employees must understand the associated security risks with working remotely.
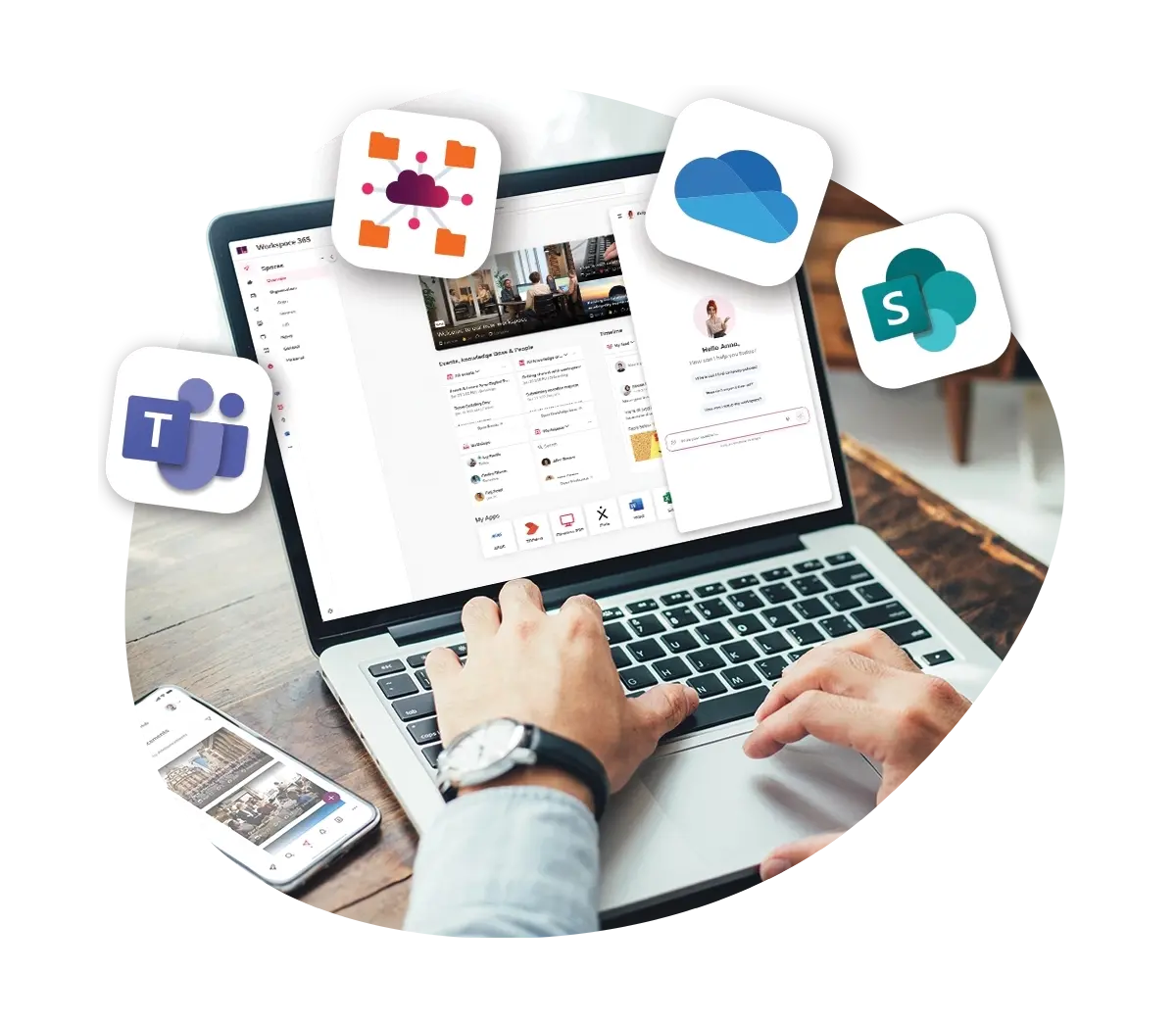
5. Create one working environment or ecosystem
Creating one, well-designed working environment or ecosystem that people actually want to log in to because it gives them easy access to all the tools and information they need to work remotely can also help reduce cybersecurity issues. Driving people through a dedicated digital workspace with a strong digital employee experience ensures people are:
- Accessing tools through Single Sign-On
- Only seeing the tools they are authorised to see
- Less likely to turn to unauthorised and risky shadow IT
- Able to see reminders and access communications about cybersecurity.
The importance of security when working remotely
It’s critical to ensure that every employee knows how to maintain security when they work remotely. IT departments and digital workplace teams should review their cybersecurity policies, make any necessary changes down to the individual application level and also drive an awareness program for employees.
Workspace 365 helps organisations navigate the security issues that come with remote working and homeworking, with the ability to create one digital workspace where employees can access everything they need, including email, through one safe workspace. Furthermore, you can add extra layers of protection by integrating additional security software.